Take it from a local Moabite: there’s no such thing as fun for everyone … unless you’re in Moab, Utah, a small town hub for outdoor adventures, tours, guided trips, National Parks, State Parks, natural and cultural history, and so much more. Do we really have to go on? Even us locals have a Moab bucketlist miles long. This list of 50 things to do in Moab, Utah, is in no way exhaustive, but will provide you with a good jumping off point as you plan your trip—or as you find yourself driving down Highway 191 toward the heart of town.
50 Things to do in Moab, Utah: written by a local
A few travel tips before we dive in! Moab is hot in the summer and cell service can be spotty outside of town. Bring lots of water and a lunch if you’re going on a day hike, and download your maps. This might be a ~hot take~, but it’s worth booking a hotel room for access to the pool and hot tub (nothing better than soaking sore muscles at the end of a long day!). And take a bit of time during your trip to learn about the impressive history of this area: let’s work together to preserve it for generations to come.
–National and State Parks–
1. Arches National Park
We know you know this one. But
Arches truly is worth every second you spend in the park: the landscape is so utterly fascinating, so unlike anything you’ve seen before. Delicate Arch is popular for a reason. And if you’re up for it, the 8-mile Devils Garden Primitive Loop Trail is a great way to spend the day.
2. Canyonlands National Park
Did you know Canyonlands National Park is split into districts? It’s just that big. The two most accessible are the Island in the Sky and Needles districts; Island in the Sky is closer to Moab. If you’re visiting I-Sky, make sure you stop by Mesa Arch (again, popular for good reason), and Aztec Butte. If you’re heading down to the Needles District, stop at Newspaper Rock along the way to see hundreds of petroglyphs, and spend the rest of the day hiking out to Druid Arch.
3. Dead Horse State Park
A gorgeous drive and even more gorgeous overlook.
–Knock something off your bucketlist–
4. Book a rafting trip down The Daily
The Daily stretch of the Colorado River is a great beginner’s whitewater trip: the rapids range from class I-III, especially if the water is high (for high water, visit in May or June).
5. Rent mountain bikes and explore the Bar M trail system
Mountain biking is fun! Don’t be intimidated by the shredder content you see online: in my opinion, mountain biking is one of the most playful sports you can do. And if an obstacle is too big, just walk it—you’re not bikin’ till you’re hikin’, as they say. Bar M is a great place to start – take a few hours and try the Rusty Spur, Bar M loop, and Lazy-EZ trails.
6. Take on Hell’s Revenge
Hell’s Revenge is one of the most popular off-roading trails in the Moab area—and dare we say, the world? If you want to see this trail for yourself, you can chat with outfitters in town to rent vehicles for a self-guided experience, book a guided tour, or hop in a massive, open air Hummer to let a guide drive the trail for you.
7. Try rock climbing at Wall Street or the Cinema
Moab is a haven for rock climbers—and many of those climbers work as guides, offering tours to, literally, show visitors the ropes. Book an experience with a climbing outfitter to really get to know the Moab sandstone.
8. Get splashed through Westwater or Cataract canyons
If The Daily isn’t enough oomph for you, book a rafting trip down Westwater Canyon or Cataract Canyon to experience huge rapids (and huge thrills!).
9. Rappel into a slot canyon
If you’re scared of heights, this experience probably isn’t for you. But if you want to explore the hidden and hard-to-get-to sides of Moab’s landscape, book a canyoneering tour with a local outfitter.
10. Challenge yourself to run a trail race
Moab is home to tons of running races at a variety of distances, from 5Ks to the legendary Moab 240. There’s no better place to run than on Moab trails! We like trail running because you’re encouraged to walk … and you can, and should, shove a lot of snacks into your snazzy trail-running vest.
11. Camp at Oowah Lake in the La Sal Mountains
If it’s too hot in Moab, escape to the nearby mountains like the locals do. You can also fish in Oowah Lake, so bring a rod!
12. See Moab from the sky
It’s hard to understand just how vast this desert landscape is until you see it from above. Treat yourself to an air tour on an airplane or helicopter to get a new perspective on the canyons you’ve explored from the ground!
13. Live your cowboy dreams
Horseback riding is another popular way to change your perspective on the Moab landscape.
14. Go “set-jetting” around landscapes featured in Western films
Did you know the Moab to Monument Valley Film Commission is one of the oldest in the world? Head out Highway 128 and you’ll recognize the landscape featured in movies like Wagon Master (1950) and Horizon: An American Saga (2024).
15. Take a night hike
Moab is a certified dark sky community – and is surrounded by the official Dark Sky Parks of Arches National Park, Canyonlands National Park, and Dead Horse Point State Park. Book an astronomy tour to explore the stars with a local expert, attend a star party at a nearby park, or just wait until darkness falls to see some of the best stars in the world.
16. See dinosaur tracks
The Mill Canyon Dinosaur Tracksite boasts tracks of eight different dinosaurs who stomped across this patch of land when Utah was part of a vast inland sea in the Jurassic period. Well-written interpretive signs help tell the story of the dinosaurs, and a boardwalk allows visitors to explore every track.
17. Drive the Upper Colorado River scenic byway
If you’ve never driven Highway 128, you’re in for a real treat. The 44-mile stretch of road takes visitors from the town of Moab along the Colorado River, passing by Castle Valley and the Fisher Towers. You’ll watch the landscape open up and morph as you wind your way to the end of the scenic byway at Dewey Bridge.
18. See petroglyphs
There’s something really special about petroglyphs: about looking at stories carved into sandstone thousands of years ago. Easily accessible sites include a site along Potash Road and the Birthing Scene petroglyph off of Kane Creek road.
19. Take an adrenaline-filled leap
Soar through the skies by leaping from a plane – or cliff! In Moab, you can book a skydiving experience, a BASE jump off a cliff, or swing off the world’s largest rope swing.
20. Go on a scenic tour
Let a local expert take the wheel to guide you through all of the must-see sights in Moab.
–Explore the landscape on must-do trails–
21. Corona Arch Trail
This arch is massive – 140 by 105 foot opening! – and the hike is fun, with a section that requires visitors to use a ladder and safety cable.
22. Fisher Towers Trail
The Fisher Towers are composed on Moenkopi and Cutler sandstones that have eroded into fantastical shapes! Allow four hours if you’d like to do the whole trail.
23. Grandstaff Canyon Trail
The Grandstaff Canyon trail leads to the magical Morning Glory Natural Bridge, winding along a creek to do so. Look out for poison ivy!
24. Hidden Valley Trail
Ascend a steep incline to find hidden valley, a valley tucked on top of the Moab Rim. This is an out and back trail – scamper along the valley for as long as you feel like it.
25. Juniper Trail
The Juniper Trail is a small loop located within the Sand Flats Recreation Area that leads visitors on a scavenger hunt looking for native flora and fauna.
26. Longbow Arch
A fun little trail located at the Poison Spider parking area that leads to the 60 foot Longbow Arch.
27. Moab Rim
Want to see sweeping views of Moab and the Colorado River? Hike up the Moab Rim Trail! This trail is tough – it’s pretty steep – but the views are worth it.
28. Amphitheater Loop
A 3 mile loop starting at the Hittle Bottom campground on Hwy 128 that requires a small gully scramble.
29. Dellenbaugh Tunnel
This trail leads to a long, tunnel-like arch.
30. Hunter Canyon
Hunter Canyon is a lovely walk: the canyon stretches for 2 miles before reaching the end. Look for the large arch on the right-hand side of the canyon about half a mile from the trailhead.
–In town–
31. Learn local history
Visits to the Moab Museum and Moab Giants are always worth it: we guarantee you’ll learn something new and surprising! Look out for special events and programs hosted by the Moab Museum, too.
32. Attend an arts or music festival
The shoulder seasons boast a number of cultural events, including the Moab Folk Festival, Moab Music Festival, Red Rock Arts Festival, and Moab Arts Festival.
33. Grab a milkshake at Moab’s oldest restaurant
Today, Milt’s Stop and Eat is just as popular as it was when it first opened in 1954. Grab a classic milkshake, fries, and a burger – and know that Milt’s sources as many ingredients as they can from local food producers!
34. Cap off your night with a visit to Moab’s dive bar
Locals will laugh that I’m including Woody’s Tavern on this list. Moab doesn’t have a ton of nightlife – it’s hard to get a liquor license in Utah – but Woody’s is always fun, and on the weekends often hosts local bands to play live music.
35. Peruse local art
Moab is an artistic haven – you can’t help but to be inspired here. Visit Moab Made and Gallery Moab to buy souvenirs and art made by only local artists.
36. Find something for everyone at the Moab Food Truck Park
You’re coming back into town from a morning hike, searching for lunch, but no one can agree where to go? The Moab Food Truck Park is home to individually owned and operated food trucks, offering a wide range of food, and a centralized place to eat.
37. Customize your Moab swag at the T-Shirt Shop
Print customized designs, ranging from silly to artistic, on any color t-shirt, sweatshirt, tanktop, long sleeve, hat, you name it.
38. Try a “dirty soda”
The dirty soda is a Utah-born beverage trend: it’s a soda base spiked with add-ins like cream, syrups, and fruit juices. Lops Pop Stop is our local dirty soda shop – get the Moab On the Rocks (Coke, cherry syrup, coconut milk, lime juice) and pretzel bites.
39. Read books by local authors
Back of Beyond Bookstore, which is independently and locally-owned, specializes in natural history and regional titles of the Colorado Plateau. But they also boast an impressive collection of popular fiction and rare acquisitions.
–Hidden Gems–
40. Swim at Ken’s Lake
Take a rest – spend a day at Ken’s Lake, a small, man-made lake just south of Moab. The lake allows dogs, fishing, and watercrafts. There’s also a campsite nearby!
41. Spend the day at Warner Lake
If Moab is too toasty, head into the La Sal Mountains. While camping near Oowah is a must, like we mentioned, a day spent at Warner Lake – fishing and exploring the nearby sections of the Whole Enchilada Trail – is never wasted.
42. Mountain bike the Raptor Route
The Raptor Route is a set of trails within the Sand Flats Recreation Area that provide an alternate exit to the Whole Enchilada trail – but are also just a ton of fun to do by themselves. Do the whole thing – Eagle Eye to Kestrel Run – or just try Falcon Flow if you’re looking for a fun, flowy, blue-black mountain bike trail.
43. Listen to live bluegrass music or catch a magic show at the Backyard Theater
The Backyard Theater is truly a Moab gem – a little stage tucked behind Zax restaurant, the Backyard Theater hosts free bluegrass music every Wednesday, Thursday, and Friday night, and a magic show on Saturdays ($10). Bring a picnic dinner – outside food and drink are welcome – and utilize the dance floor.
44. Enjoy a local beverage
The Moab Brewery (beer & spirits), Spanish Valley Winery (wine), and Wild Bloom Fermentations (kombucha) each offer locally-brewed beverages. If you’re looking for locally-roasted coffee beans, you can find them at Curve Coffee, Moab Coffee Roasters, Fresh Moab Coffee, and Dave’s Corner Market!
45. Thrift your new favorite shirt
Moab has excellent thrift stores, including WabiSabi, Underdog Thrift Store, Moab Gear Trader, and Radium Alley Thriftique.
46. Drink from a natural spring
The legend around Matrimony Springs – a natural spring located on Highway 128 – is that if you drink the water, you’ll never leave Moab.
47. Sled the sand dune
The giant sand dune located on the other side of the highway from the entrance gate to Arches National Park is hard to miss. Bring a sled, or just walk up and roll down the dune – and see if you can make the trek up to the very top!
48. Play in a park
The Moab landscape is its own playground – but if you need a place for kids to run around, head to Rotary Park (which has a playground, volleyball net, basketball court, gazebo, and musical structures that kids and adults will have a blast experimenting with) or Lions Park (which is home to a playground and bouldering structures).
49. Get hands-on with local geology – and take it home
In 1960, Lin Ottinger – a uranium miner turned tour guide – opened the Moab Rock Shop, a treasure trove of rocks, minerals, and fossils. Many of Ottinger’s discoveries have been donated to museums and universities, but others are hosted in the rock shop!
50. Fall in love with a Moab local and never leave
Only slightly joking.
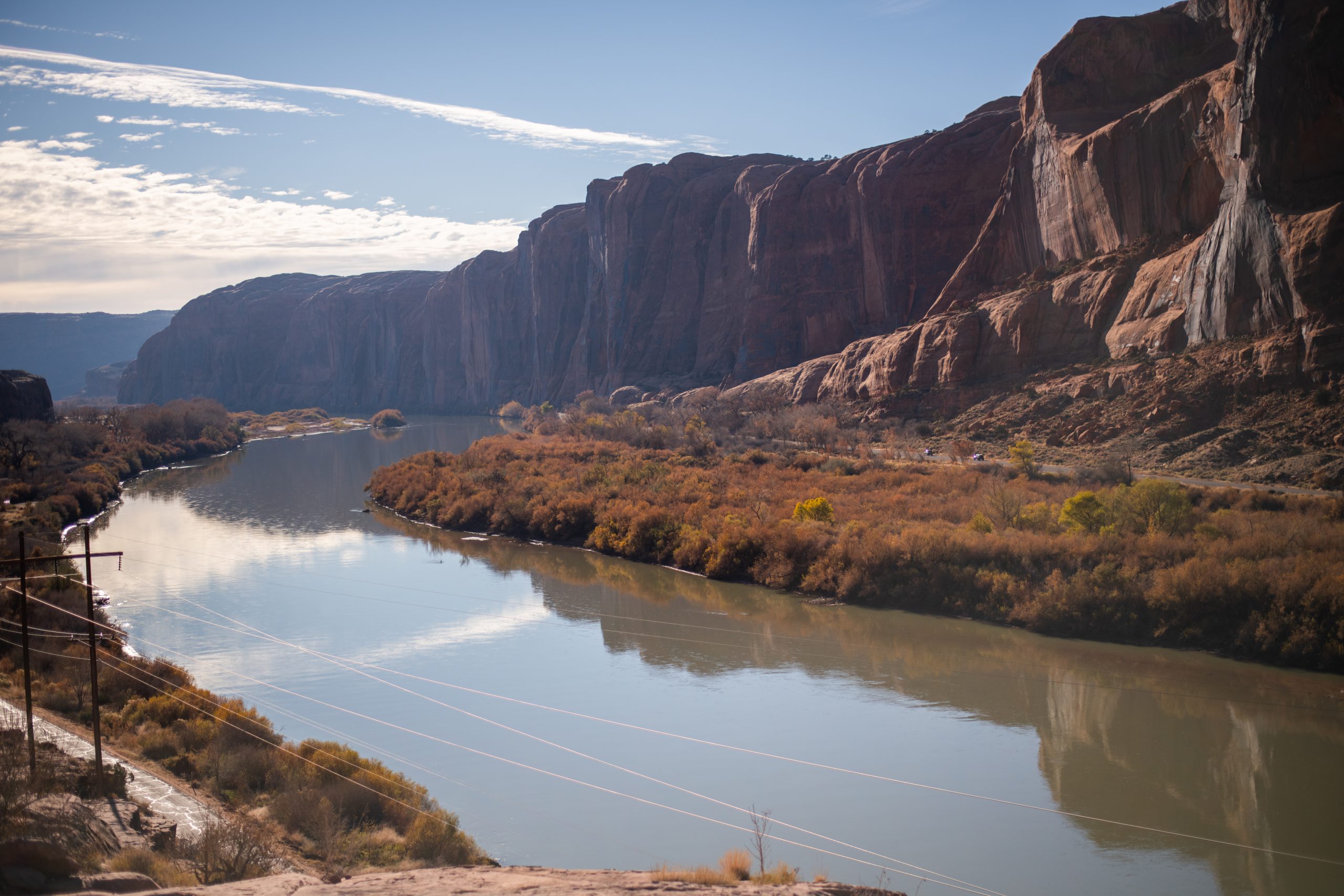 The view of the Colorado River from the Moab Rim Trail.
The view of the Colorado River from the Moab Rim Trail.
By local experts at Discover Moab
My favorite place in the world is just a few minutes outside of downtown Moab, Utah. I turn off Main Street at Kane Creek Boulevard, a street that winds past the movie theater and through a few small neighborhoods before it lands next to the Colorado River. The road leads to campsites, canyons, hiking trails, biking trails, petroglyphs, off-road routes, climbing crags – Kane Creek Boulevard is one of Moab’s hidden gems, and it’d be easy to spend days here, especially if you snag a camping spot. It’s well-worth adding a day to your Moab trip just to explore this unique zone.
Something to keep in mind with activities down Kane Creek: there is very spotty cell service in this area! Download your maps beforehand and consider bringing a satellite communications device.
And another note: many of the trails get very hot in the summer – there isn’t a ton of shade out here – so be ready for the weather and bring snacks and water with you.
Places to camp along Kane Creek: Kings Bottom, Hunter Canyon/Spring Canyon, The Ledge
Things to do along Kane Creek Boulevard – choose your own adventure style
Hike or off-road the Moab Rim Trail
Keep an eye out for a trailhead shortly after the road turns left and starts following the Colorado River. This is the Moab Rim Trail, a hiking and off-roading route that offers stunning views of the Colorado River and the town of Moab. It’s one mile to reach the stop, but it’s a steep mile – the hiking route is called
“The Escalator” for a reason. Watch for local Moabites who run it.
Explore Moonflower Canyon
Just after Kings Bottom campground is Moonflower Canyon, which provides a shaded and cool walk through a beautiful, tree-lined canyon. This canyon floods during monsoon season in late summer: when you make it to the end, peer up at the canyon walls and you’ll get an idea of how large the cascade of water falls down into the canyon.
Before leaving the parking lot, head over to the right side (as you’re looking at the canyon) to spot your first petroglyphs of the day. Here’s
what to know about petroglyphs before you go.
Hike or off-road at Pritchett Canyon
Pritchett Canyon provides another thrilling off-road or hiking experience. It’s the hardest off-road trail in Moab, so you may prefer to hike it–hiking three miles (six out and back) will get you near a number of arches and bridges formed in the rocks. The start of the canyon passes through private land, so you have to pay a small fee. These trails are a bit harder to follow, so make sure you do your
research beforehand.
Explore Jackson’s Trail
Park at a large parking lot just past Pritchett Canyon for access to Jackson’s Trail. This is a bike-accessible trail as well, but mountain bikers will be coming down the trail, so keep an eye out for them as you explore. The
trail follows the Colorado River for a mile or so, then switchbacks its way up to the top of a mesa, where it’ll connect to a few other trails. Stop here to take in views of the river, or continue on to the Rockstacker trail to find Pothole Arch. Beware of getting lost, and of a short icy stretch in the winter.
Bike, hike, climb, off-road, and watch basejumpers at the Amasa Back/Captain Ahab/Hymasa trailhead
Pull off at the Amasa Back/Captain Ahab/Hymasa trailhead on a nice, not-windy day and you’ll likely be able to spot basejumpers leaping from Tombstone Rock across the road. This trailhead is a hub of activity: It leads to a world-class mountain biking trail system and a popular off-road route. The most popular mountain biking trail accessible here is
HyMasa/Captain Ahab: if you’re an expert-level mountain biker, this trail is not to be missed. Thousands of bikers come to this area each year to experience it! If you’re not on a bike, this trail makes for a lovely hike or trail run as well. You’ll likely pass by off-roaders testing their skills along the Cliffhanger road.
Rock climbers can also spend a few hours enjoying the
Abraxas Wall, accessible from this trailhead, which has 10 trad climbs ranging from 5.10 to 5.11d.
This is a good spot for a picnic lunch!
Peer into the past at the Birthing Scene petroglyph
One of the most captivating petroglyphs in Moab (in this writer’s opinion) is the birthing scene petroglyph, which was carved onto a large boulder. The petroglyph shows, as you can guess, a birthing scene: there are two humanoid figures depicted, along with depictions of feet and animals. It’s a beautiful glimpse into the past and the lives of the people who first lived in this area.
Remember: do not touch the petroglyphs! We want to
preserve these rocks as long as we can. Scratching on rocks causes irreparable damage and is illegal.
Scramble up to Funnel Arch (only if you have route-finding skills)
Continuing past the Birthing Scene petroglyph, you’ll find a small pull-off on the road to the left. This is the small trailhead to the Funnel Arch trail, a short and fun trail that leads to an impressive arch. This trail requires significant route-finding skills – the trail dips in and out of sight – and there’s a challenging rock climbing scramble right at the start.
Rock climb at the Ice Cream Parlor climbing wall
The
Ice Cream Parlor climbing wall offers 45 sport and trad climbs from beginner 5.7 routes to a few challenging 5.12 PG13s. It’s south facing, so if you plan to climb, get here early to avoid the scorching sun – or visit during a sunny winter day, when the warm rock provides balmy respite from cold temperatures. This wall truly provides something for everyone, no matter what skill level climber you are.
Continue on to watch the canyon open up into a wide desert landscape – and find a few more camping options
The Ledge campsites are further down the road. Past here, the road turns into a 4×4 road – off-roaders will enjoy going through Hurrah Pass and along Lockhart Basin road as part of the
Chicken Corners route.
 The Moab Music Festival in late August and early September offers floating concerts.
The Moab Music Festival in late August and early September offers floating concerts.
By local experts at Discover Moab
According to
Conde Nast Traveler, athletic adventures are in: travelers are bringing their sports with them, or seeking out destinations where they can really play. We expect that Moab, which has long been a hub of outdoor sports like mountain biking, trail running, and white water rafting, will see this trend guide the activities of our 2025 visitors. Other trends relevant to our little slice of the desert southwest? Detour destinations–think “getting a little lost on purpose” and “spotting a sign for an ancient ruin and deciding that your hotel can wait a bit”–cowboy core travel–“horse riding trips and camping under the stars”–and night tourism–Moab is a perfect spot to chase the stars.
If you’re looking to add a bit of structure to your trip (there are so many things to do in Moab, it can feel a bit overwhelming!), consider planning your Moab trip around one of the many music festivals, off-road gatherings, trail running races, rodeos, or a free entrance day to our nearby
national parks.
Here’s an overview of not-to-miss events in Moab this year, or check out our
full events calendar!
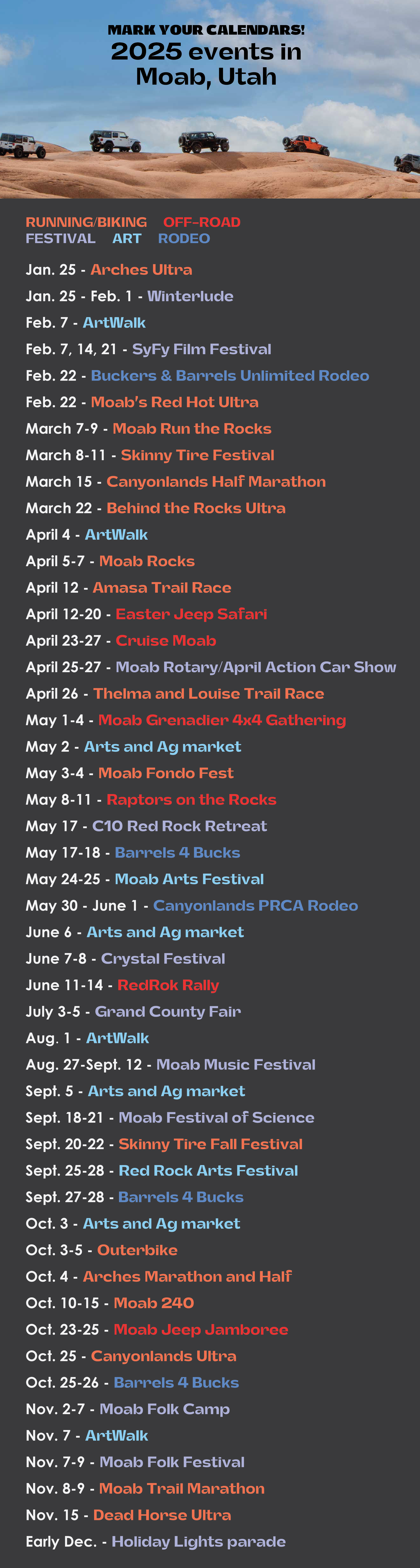
FREE NATIONAL PARK ENTRANCE DAYS
Monday, January 20 – Martin Luther King Jr. Day
Saturday, April 19 – First day of National Park Week
Thursday, June 19 – Juneteenth National Independence Day
Monday, August 4 – Anniversary of the Great American Outdoors Act
Saturday, September 27 – National Public Lands Day
Tuesday, November 11 – Veterans Day
ANNUAL CULTURAL AND OUTDOOR EVENTS
January
January 25: Arches Ultra
The Arches Ultra offers four distances of a running race: 9K, half marathon, 50K, and 50 mile. The courses are lower elevation, taking runners along the border of Arches National Park using the Bar M, Klonzo, and Klondike Trail Systems.
January 25 to February 1: Moab Music Festival “Winterlude”
Community and education take centerstage during the Moab Music Festival’s Winterlude, a week of workshops and concerts. Guest ensembles include W4RP, Pascal Le Bouef, and Sara Carswell. Workshops include a potluck and play (bring an instrument and a dish!) and musical coaching. There will be two formal concerts, plus a casual “sips and sounds.”
February
February 7: ArtWalk
Explore art exhibits all over town during ArtWalk! Featured locations this year include the Grand County Library, Moab Museum, Gallery Moab, Moonflower Co-op, and Moab Arts.
February 7, 14, and 21: Moab SyFy Film Festival
Join the Moab community in enjoying classic films of the science fiction genre, for free! Event-goers are encouraged to dress up as they watch Day of the Triffids (1963) on Feb. 7, When Worlds Collide (1951) on Feb. 14, and Europa Report (2013) on Feb. 21.
February 22: Buckers & Barrels Unlimited Rodeo
Bull teams, barrel racing, bronc riding: attend an action-packed rodeo day in Moab. Don’t miss out on the chance to witness some of the best riders in the country showcase their skills, whether you’re a seasoned cowboy or just looking for a bit of excitement!
February 22: Moab’s Red Hot Ultra
Runners of Moab’s Red Hot Ultra choose between four distances: 15K, 33K, 50K, and 50 mile. Each course utilizes a mixture of double and single track trails over a variety of terrain and elevation.
March
March 7-9: Moab Run the Rocks
A three-day trail running race on singletrack trails around Moab with two distances: 85K and 53K.
March 8-11: Skinny Tire Festival
A road biking event that will take bikers through Arches National Park, up to Dead Horse Point State Park, and alongside the Colorado River. $15 for every paid registration goes toward the Moab Cancer Treatment Center, and bikers can register for all four days or join just two.
March 15: Canyonlands Half Marathon and 5 Mile Run
Celebrate 50 years of the Canyonlands Half Marathon in 2025! This race is known locally as the Moab Half Marathon: the first event was run on May 1, 1976 and had 22 finishers (including a dog). The course follows the Colorado River and has been named one of the world’s greatest races.
March 22: Behind the Rocks Ultra
The Behind the Rocks Ultra (distances: 10 mile, 30K, 50K, 50 mile) starts and ends at the Behind the Rocks Trail, following the Behind the Rocks Wilderness Study Area. The courses traverse remote trails, sandy washes, and double and single track trails.
April
April 4: ArtWalk
Explore art exhibits all over town during ArtWalk! Featured locations this year include the Grand County Library, Moab Museum, Gallery Moab, Moonflower Co-op, and Moab Arts.
April 5-7: Moab Rocks
A three day mountain biking race covering 76 miles and over 7,800 feet of elevation across classic Moab trails. A race, festival, family-friendly vacation, and adventure all rolled into one weekend!
April 12: Amasa Trail Race
Explore the Amasa Back trail system on foot during the Amasa Trail Race at three distances: 10K, 15K, and 25K.
April 12-20: Easter Jeep Safari
The Red Rock 4 Wheelers most popular event returns on April 12: the Easter Jeep Safari. Attendees are invited to join trail rides departing from Moab each day to explore the vast array of trails that the area has to offer with a community of likeminded souls!
April 23-27: Cruise Moab
A Toyota Land Cruiser Association sanctioned event that has occurred every year since 1999. Attendees will explore off-road trails around Moab together during guided trail runs.
April 25-27: Moab Rotary/April Action Car Show
Gather with fellow car enthusiasts to explore the best cars the Moab region has to offer. There are typically 13 award classes for cars, including best muscle car, best truck, best hot rod, and best import; attendees can expect to see modified and stock cars and motorcycles dating back to 1900.
April 26: Thelma and Louise
A women’s running event with races at four distances: 15K, half-marathon, marathon, and 50K – because every girls’ weekend should include an exciting challenge!
May
May 1-4: Moab Grenadier 4×4 Gathering
Bring your Grenadier Station Wagon to Moab to explore the epic 4×4 trails this area has to offer – and meet a community of off-roaders to adventure with.
May 2: Arts&Ag Market
Peruse locally-grown produce and artisanal goods with live music at this evening market.
May 3-4: Moab Fondo Fest
Prepare for a remarkable cycling experience during one of Utah’s premiere Gran Fondo-style events. The course will take riders on a journey through challenging terrain and captivating scenery.
May 8-11: Raptors on the Rocks
Explore the off-road trails in the Moab area in your Ford Raptor and enjoy the camaraderie of others who are equally passionate for this off-road vehicle! Four days of world-class off-roading, giveaways, and an opportunity to learn from guides.
May 17: C10 Red Rock Retreat
A charity event for the City of Moab and the Grand County Search and Rescue Team! Peruse classic GM trucks under the red rock cliffs and peruse items from a large silent auction.
May 17-18: Barrels 4 Bucks
See the best barrel racers in the region compete during the Barrels 4 Bucks event in Moab!
May 24-25: Moab Arts Festival
Peruse a broad selection of original art – textiles, fine art, glasswork, jewelry, metal and wood – created by local and regional artists! There is also a kids corner with activities for children, live performances, live music, and a beer and wine garden. The arts festival is free to attend!
May 30 – June 1: Canyonlands PRCA Rodeo
The Canyonlands PRCA Rodeo is part of the All American ProRodeo Series and is a member of the PRCA Pro Rodeo Cowboy Association. Classic rodeo events include steer wrestling, saddle bronc riding, team roping, calf roping, barrel racing, bull riding, and bareback riding.
June
June 6: Arts&Ag Market
Peruse locally-grown produce and artisanal goods with live music at this evening market.
June 7-8: Crystal Festival
A rock, gem, and mineral festival with a vendor market and rockhounding trips!
June 11-14: RedRok Rally
A rally for UTV enthusiasts! Attend guided trail rides (including Hells Revenge and Fins N’ Things), peruse vendor markets, and enjoy live music with likeminded community.
July
July 3-5: Grand County Fair
Fair activities include eating contests, relay games, exhibits, sporting tournaments and derbies, and a car show! Admission is free.
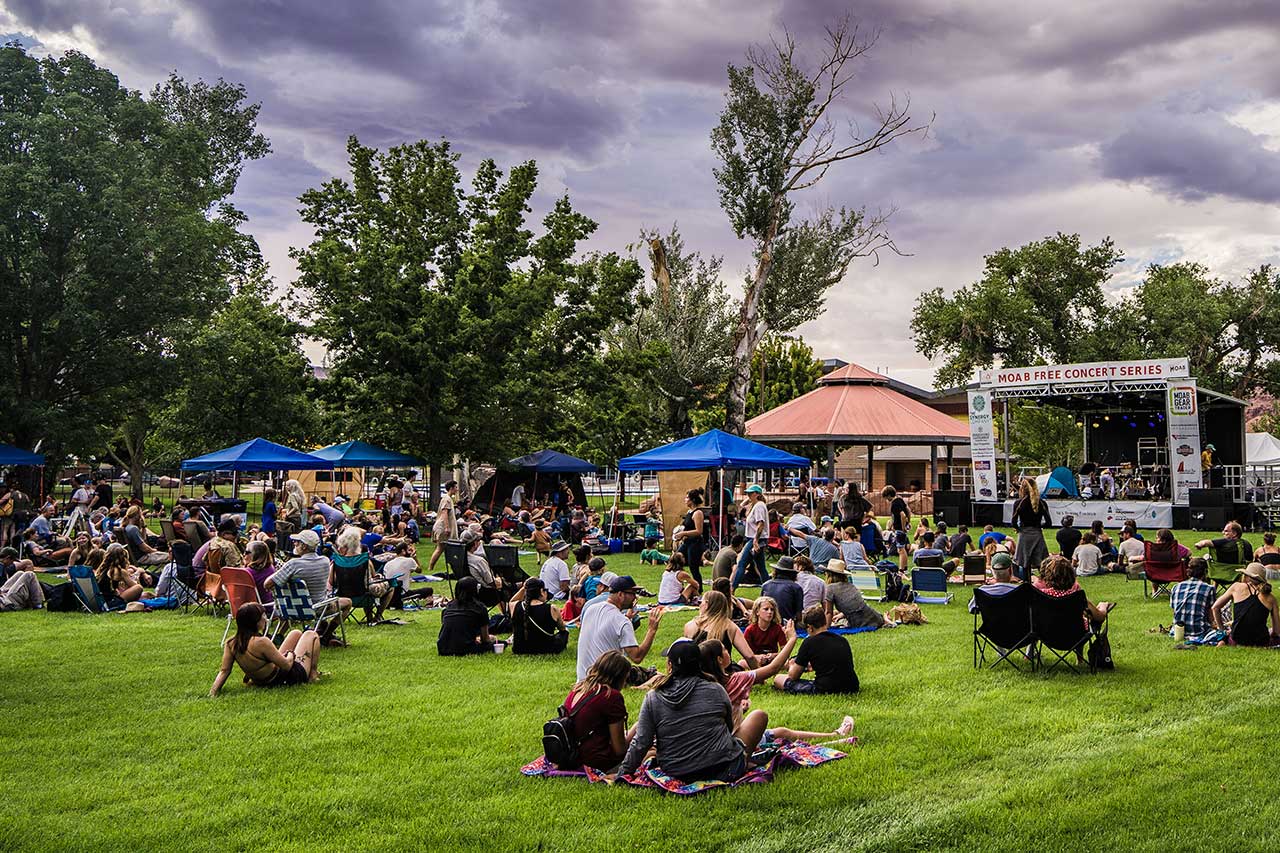 The Moab Free Concert series takes place every summer.
The Moab Free Concert series takes place every summer.
August
August 1: ArtWalk
Explore art exhibits all over town during ArtWalk! Featured locations this year include the Grand County Library, Moab Museum, Gallery Moab, Moonflower Co-op, and Moab Arts.
August 27-September 12: Moab Music Festival
Enjoy performances of chamber music, jazz, and Latin music within the beautiful red rock landscapes near Moab. That’s right: this is a music festival performed in wilderness and historic venues unlike any other! Concerts range from family-friendly music in local parks to accessible-by-jet-boat-only grottos carved from rocks where musicians play odes to timeless masterpieces.
September
September 5: Arts&Ag Market
Peruse locally-grown produce and artisanal goods with live music at this evening market.
September 18-21: Moab Festival of Science
A fantastic variety of free events showcasing the wonders and value of science, with a special focus on Colorado Plateau science! Events include activities with the National Park Service; astronomy, archaeology, and geology tours; and keynote speakers.
September 20-22: Skinny Tire Fall Festival
A brand new event showcasing Moab’s full geographical beauty to road cyclists from across the country! Ride to the Bull Canyon Overlook, through the River Portal, and up to Dead Horse Point State Park.
September 25-28: Red Rock Arts Festival
Three days of art celebrating a theme announced in spring 2025! Programming will feature collaborative projects, art experiences, music performances, a community art show, and an artisan vendor market: the perfect way to get a taste for Moab’s exuberant arts community.
September 27-28: Barrels 4 Bucks
See the best barrel racers in the region compete during the Barrels 4 Bucks event in Moab!
October
October 3: Arts&Ag Market
Peruse locally-grown produce and artisanal goods with live music at this evening market.
October 3-5: Outerbike
A mountain bike festival that is not to be missed! Experience the red rock beauty and world-class mountain biking trails in the desert sunshine before winter sets in. Shuttles, catered lunches, vendor market, and bike demos are included in registration.
October 4: Arches Marathon and Half
Runners can explore the Behind the Rocks Wilderness Study Area and the remote Picture Frame Arch over four distances: 15K, half marathon, marathon, and 50K.
October 10-15: Moab 240
Runners will complete 240 miles in one loop around Moab and the surrounding areas with a 117 hour cutoff.
October 23-25: Moab Jeep Jamboree
Attendees will spend the weekend exploring offroad trails around Moab with a guide, then enjoy dinner together.
October 25: Canyonlands Ultra
Runners will immerse themselves in the nearby landscapes through six offered course lengths: 100K, 50 mile, 50K, marathon, half marathon, and 15K.
October 25-26: Barrels 4 Bucks
See the best barrel racers in the region compete during the Barrels 4 Bucks event in Moab!
November
November 2-7: Moab Folk Camp
A week of music classes for musicians of every skill level! Classes last year included a singing workshop, guitar theory, beginning dobro g-tuning, songwriting 101, basic jazz, and beginning mandoline with a variety of instructors. Attendees will complete four classes per day and evening activities.
November 7: ArtWalk
Explore art exhibits all over town during ArtWalk! Featured locations this year include the Grand County Library, Moab Museum, Gallery Moab, Moonflower Co-op, and Moab Arts.
November 7-9: Moab Folk Festival
Over 10 bands and musicians play at the annual Moab Folk Festival, a celebration of folk music in downtown Moab. Each festival includes two days of outdoor concerts, but also free community concerts, student assemblies, music workshops, and artist residency programming.
November 8-9: Moab Trail Marathon
An unforgettable run through the Kane Creek Canyon area at four distances: marathon, half marathon, 10K adventure run, and kid’s K. In 2024, this race was the host of the USATF trail half marathon national championships and collegiate trail running championships.
November 15: Dead Horse Ultra
Runners will explore the Magnificent 7 singletrack trail system over four distances: 15K, 30K, 50K, and 50 mile.
December
December 6: Holiday Light Parade
Kick off the holiday season with the electric light parade on Main Street, a chance to see local floats decorated with hundreds of holiday lights.
Save this graphic!
If you’re planning a trip to Moab, you’re likely aware of its reputation as an oasis for outdoor recreation. But the city also has a lot to offer when it comes to dining, arts, and culture. Read on to make the most of your three-day trip.
DAY 1 – PARKS TOUR
Morning: Canyonlands National Park
Start your day at Canyonlands National Park. Roughly 30 miles outside Moab, the Island in the Sky District provides sweeping canyon views and stunning red rock panoramas. In a few hours’ time, you can drive the park’s 20 miles of paved roads to Grand View Point, Green River Overlook, and Upheaval Dome and hike the Grand View Point, Mesa Arch, and Upheaval Dome Overlook trails. Get up early to catch sunrise at the Mesa Arch or any of the other viewpoints inside the park.

Mesa Arch

Green River Overlook
Hiking Options
- Easy: Mesa Arch (0.6 mi/1 km) Recommended before sunrise.
- Moderate: Grand View Point (1.8 mi/2.9 km)
Lunch: Dead Horse Point State Park
On your way back from Canyonlands, don’t miss Dead Horse Point State Park. Head to Dead Horse Point Overlook to take in the view of the Colorado River and the surrounding pinnacles and buttes that make up one of the most photographed scenic vistas in the world. Bring a picnic lunch and stop in the visitor center.
Hiking Options
- Easy: The Colorado River Overlook (1 mi/1.6 km)
- Moderate: The Bighorn Overlook Trail (3 mi/4.8 km)

Dead Horse Point State Park

Moab Giants Museum & Dinosaur Park
Afternoon: Moab Giants Museum & Dinosaur Park
Fun for the whole family, Moab Giants Museum & Dinosaur Park is the first of its kind worldwide! Take a journey back through time with a 3D cinema experience and a half-mile trail featuring more than 130 full-size reconstructions of dinosaurs and their tracks. Inside the Tracks Museum, you’ll find interactive learning touch screens, games to play, and visually stunning educational exhibits. These exhibits also include insights into the history and prehistory of the Moab area and windows into Moab Giant’s research labs.
Evening: Dinner in Town
After a full day of exploring, head into town to refuel. Moab is home to a variety of cuisines and local eats. For family-friendly dining, try Moab Diner or Moab Grill. To enjoy a local brew with your meal, visit Moab Brewery or Proper Brewing Moab.
DAY 2 – GET ACTIVE
During the Day: Choose Your Own Adventure
Spend the day recreating in Moab’s red rock wilderness. Thanks to the numerous local guides and outfitters, visitors of all ability levels can enjoy activities to the fullest, or try something new! Some popular options include:
- Mountain Biking: Cover more ground by hopping on a bike and hitting the trail. Moab offers some of the greatest mountain biking in the world, with a variety of trail options for any experience level. From the highly technical Slickrock Bike Trail to the easy-riding Bar-M Loop Trail, you’ll enjoy incredible scenery and a good work out.
- Colorado River Water Recreation: Whether you’re looking for an intense whitewater experience or a more leisurely float, there’s a section of the river for you. Choose from rafting, kayaking, canoeing, or paddle boarding, then start paddling to get a whole new perspective on the area from the Colorado River’s red rock-lined waters.
- Horseback Rides: For a truly authentic Western experience, nothing beats touring the rugged desert by horseback. Follow in the footsteps, or hoofprints, of cowboys as part of a guided trail ride to stunning landmarks such as Castle Rock and Fisher Towers.
- Scenic Flights: The wild and untamed landscape of southern Utah is so vast, it’s nearly impossible to see it all. However, even an hour-long scenic flight allows you to experience spectacular views over thousands of square miles of canyon country. No other mode of transportation will allow you to see so much in such a short period of time.

Bar-M Trail

Scenic Flight
In the Evening: Wind Down
Toast to a day well spent at Moab’s own local winery. Visitors may be surprised to learn Moab’s long growing season, coupled with its fertile, sandy soils, has resulted in delicious white German-varietal wines. Spanish Valley Vineyards & Winery specializes in these single-vineyard estate-bottled wines, which means they grow the grapes, ferment, and bottle the wine all at their single location. Stop by to enjoy the sunset with a tasting or tour.
DAY 3 – MORE TO EXPLORE
Morning: Experience History
After back-to-back adventure-filled days, sleep in and grab a leisurely breakfast. For a full spread, visit Jailhouse Cafe. If you’re in need of a quick bite, grab coffee and one of the deliciously inventive doughnuts at Doughbird.
To learn more about Moab’s beginnings, visit the Moab Museum. The museum interprets the stories of the Moab area, from histories of the first inhabitants of the Moab Valley to geology to uranium mining, and include many facets of Moab’s past, present, and future.
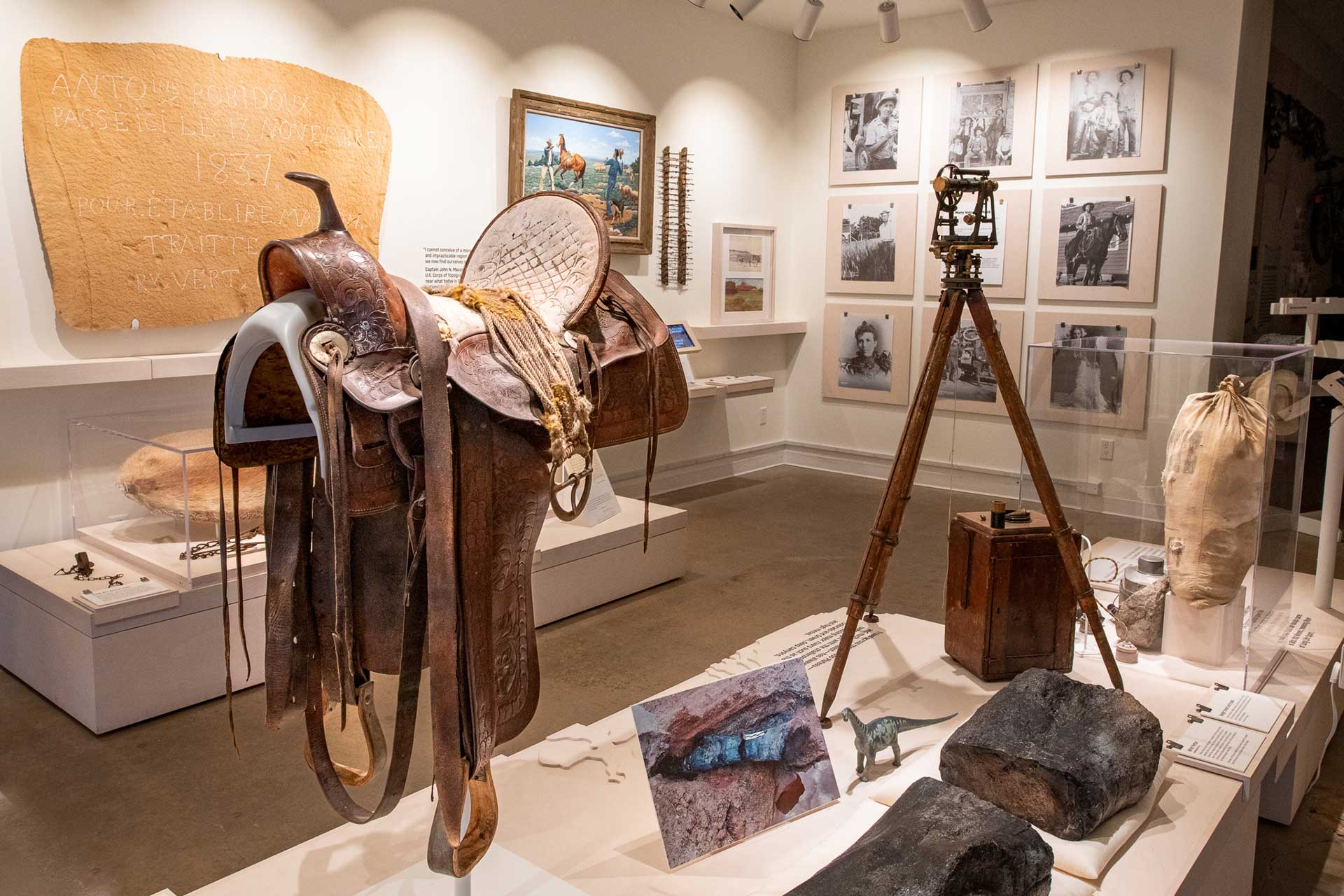

Moab Museum

Arches National Park
–
Afternoon: Arches National Park
Next, make your way to Arches National Park, home to the world’s largest concentration of sandstone arches located just five miles from downtown Moab. You can drive the entire park in three hours with 10-minute stops at each viewpoint and a short hike at the Windows section of the park. If you’re planning to visit between April 1 and October 31, you will need to make a timed entry reservation for peak times before heading to the park.
Hiking Options
- Easy: Double Arch (0.5 mi/0.8km), Landscape Arch (2 mi/3.2 km)
- Moderate: Delicate Arch (3 mi/4.8 km) This hike is usually crowded; visiting at sunrise or sunset is best.
Evening: Art and Souvenirs
For a unique dinner option, visit the Moab Food Truck Park. With 14 different food trucks offering a variety of options, there’s something to please everyone’s palate. Spend the rest of the evening wandering the shops and art galleries on downtown’s Main Street, where you’ll find everything from landscape paintings and photography to jank art (sculptures made from desert finds) and locally made goods. Then, end your trip on a sweet note with dessert at La Michoacana.

Downtown Moab

Moab Art
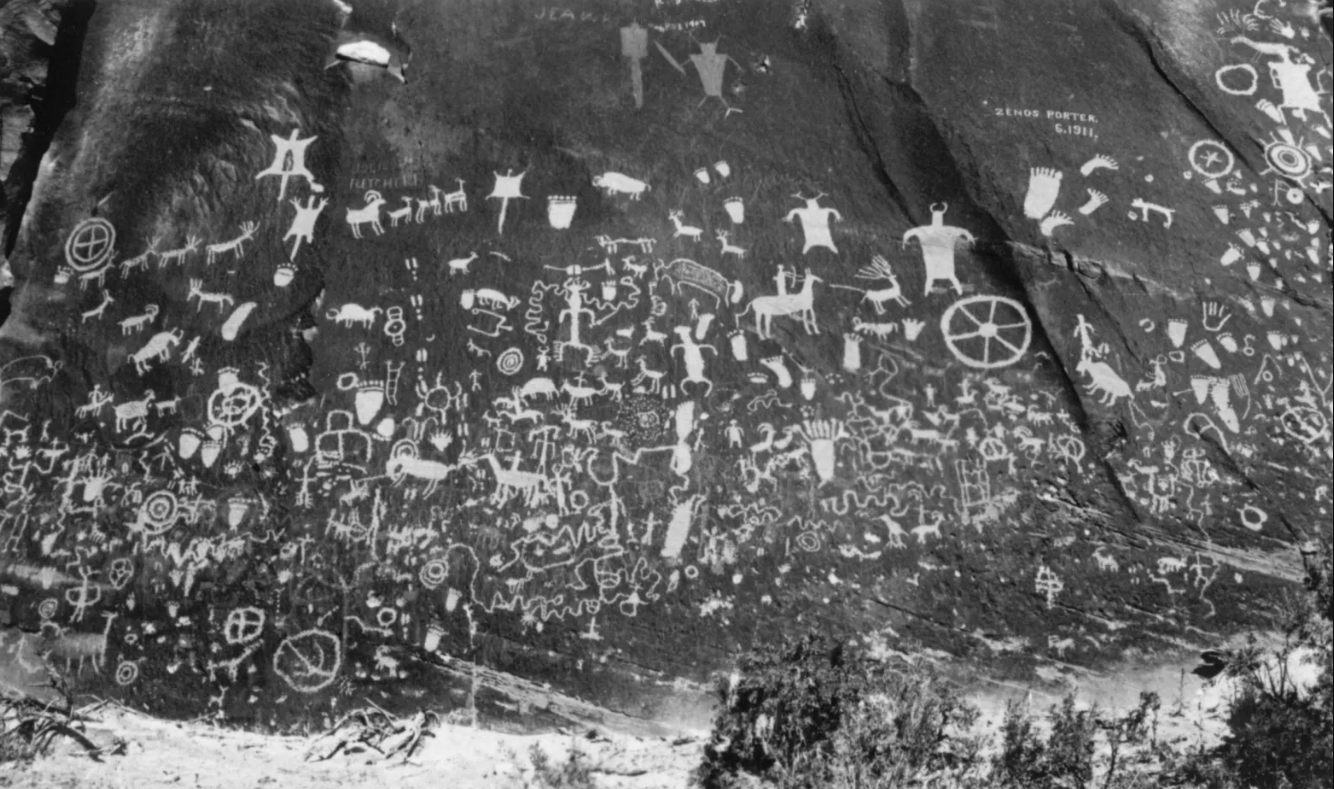 Newspaper Rock [Moab Museum Collection, Elaine Peterson Collection]
Newspaper Rock [Moab Museum Collection, Elaine Peterson Collection]
This is canyon country, a landscape defined by the forces of nature that have carved their way through the red sandstone for millions of years and still continue to perform their work. The human history of this landscape carries a similar throughline: Rock inscriptions carved on canyon walls over thousands of years lend whispers of the history of the people who came before.
Petroglyphs and pictographs across the region preserve thousands of years of human history, spanning many cultures over time. There is much to be learned from these marks pecked or painted onto canyon walls, and they remain important sites for Native communities today.
What is the difference between petroglyphs and pictographs?
Petroglyphs—which are generally more abundant in this area—are images created by carving, engraving, or scratching upon the surface of the rock. Pictographs are painted, consisting of pigment applied to the surface of the stone. While certain panels may have originally been a combination of petroglyphs and pictographs, the windswept sandstone now primarily reveals petroglyphs.
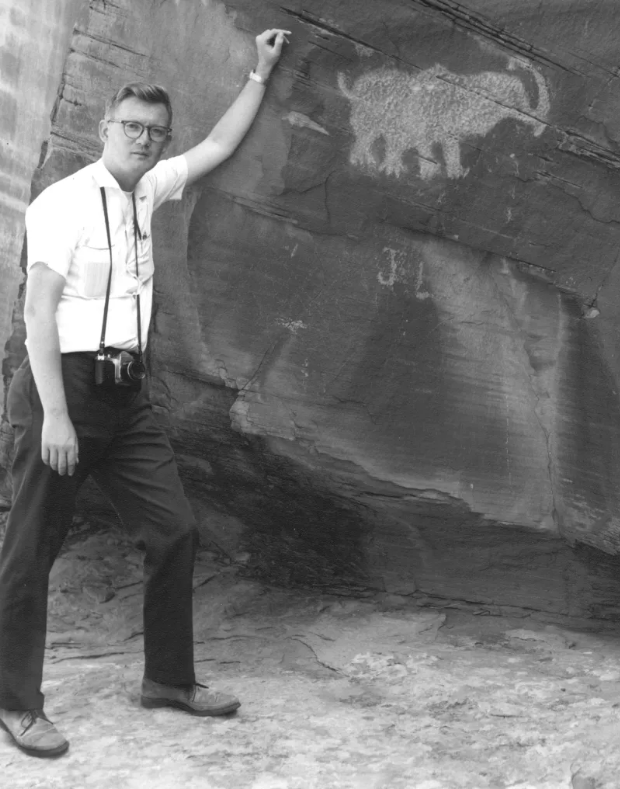 Located downriver from Moab, this rock carving is thought by some to resemble a mastodon, leading some to believe that it was created by people living in the Moab Valley during the late Ice Age. Others interpret the panel as a bear with a fish in its mouth. [Moab Museum Collection, Elaine Peterson Collection]
Located downriver from Moab, this rock carving is thought by some to resemble a mastodon, leading some to believe that it was created by people living in the Moab Valley during the late Ice Age. Others interpret the panel as a bear with a fish in its mouth. [Moab Museum Collection, Elaine Peterson Collection]
What is known about petroglyphs and pictographs?
There are numerous ways to interpret meaning, and inevitably, much of it remains a mystery to visitors today. Native groups with Ancestral ties to the region can offer perspective and interpret meaning from rock writings left many generations ago. Archaeologists also offer a set of ways to interpret these sites.
In the summer of 2021, the Moab Museum presented a temporary exhibition called “Stories on Stone: Interpreting & Protecting Moab’s Rock Imagery” in collaboration with Utah Humanities. The exhibit showcased perspectives about four prominent Moab-area petroglyph panels from Hopi guide and interpreter Bertram Tsavadawa and archeologist Don Montoya.
“There’s always variations of understanding of how sites will be utilized by the Ancestors,” Tsavadawa explained in the exhibit, adding “as a Hopi person, coming from northeastern Arizona to visit and see these sites here, it is reconnecting.”
In a video made with the Museum and the Utah Humanities Council’s Humanities in the Wild initiative, Tsavadawa drew connections between petroglyphs of wavy lines at Moonflower Canyon to the abundant water nearby.
“Water sustains life. Wherever there’s water, you’ll find maybe an Ancestral site, occupation location, or where they were visiting or making their pilgrimages to conduct ceremony, or connect back to nature,” Tsavadawa explained.
Archeologists also offer ways of understanding these traces of the past. A variety of scientific dating methods, including carbon dating, may determine the ages of pictograph pigments. In the absence of pigment, archaeologists can use optically-stimulated luminescence, which tells how long quartz sediments have been exposed to light. Archeologists also recognize distinctive aesthetic styles associated with different periods, such as the Barrier Canyon Style, which allows them to determine the spatiotemporal extent of cultural groups.
Rock imagery sites remind us that history exists beyond the bounds of a museum collection space. Stewardship of sites remains an ongoing topic of community conversation. In April 2021, Birthing Rock, a prominent rock imagery site along Kane Creek Road, was vandalized, inciting community outrage. The vandalism was the second publicized instance in 2021 of petroglyphs in Moab being damaged, the first being a rock climber bolting a route near a 1,000-year-old petroglyph panel near Arches National Park.
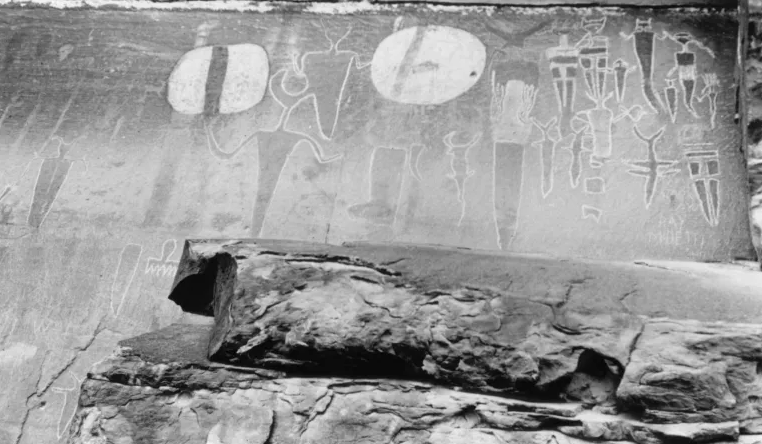 The pictographs at the mouth of Courthouse Wash as it enters the Colorado River represent the Barrier Canyon style, also found at Sego canyon near Thompson Springs. This image was taken before the panel was defaced in 1980. Following the vandalism, the National Park Service cleaned the panel, and restoration work revealed older pictographs beneath the white shields. [Moab Museum Collection, Elaine Peterson Collection]
The pictographs at the mouth of Courthouse Wash as it enters the Colorado River represent the Barrier Canyon style, also found at Sego canyon near Thompson Springs. This image was taken before the panel was defaced in 1980. Following the vandalism, the National Park Service cleaned the panel, and restoration work revealed older pictographs beneath the white shields. [Moab Museum Collection, Elaine Peterson Collection]
Why does it matter to protect rock imagery and Ancestral sites?
In the words of the Bears Ears Intertribal Coalition: “To the untrained eye, these archaeological features can sometimes be hard to recognize, but their importance to science, as well as tribal descendants, is immense…More than just a library of human history, this place remains vital to tribal communities across the Colorado Plateau as a place of subsistence, spirituality, healing, and contemplation.”
When visiting these sites, make sure to observe proper visitation etiquette to preserve this history and pay respect to the enduring connections these places provide for Native communities today. These tips, from the Museums of Western Colorado, provide guidance to visitors today:
– Visit rock art sites with respect. Many cultures today see rock art as being just as sacred as it was when it was created.
– Do not touch images. The oils on your hands cause damage that cannot be fixed.
– Take only pictures. Paper rubbing and latex molds cause irreversible damage.
– Respect private property rights.
– Leave archaeological clues found near rock art panels in place. Artifacts such as projectiles can help archaeologists better understand and date the age of panels.
– Report any vandalism to a local land agency such as the Bureau of Land Management, Forest Service, and Park Service.
The Moab Museum is dedicated to sharing stories of the natural and human history of the Moab area. To explore more of Moab’s stories and artifacts, find out about upcoming programs, and become a Member, visit MoabMuseum.org



 The view of the Colorado River from the Moab Rim Trail.
The view of the Colorado River from the Moab Rim Trail.














 Newspaper Rock [Moab Museum Collection, Elaine Peterson Collection]
Newspaper Rock [Moab Museum Collection, Elaine Peterson Collection]

